Difference between revisions of "AWS Secrets Manager"
Tag: Reverted |
Tag: Manual revert |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== The services provided by Secret Manager == | == The services provided by Secret Manager == | ||
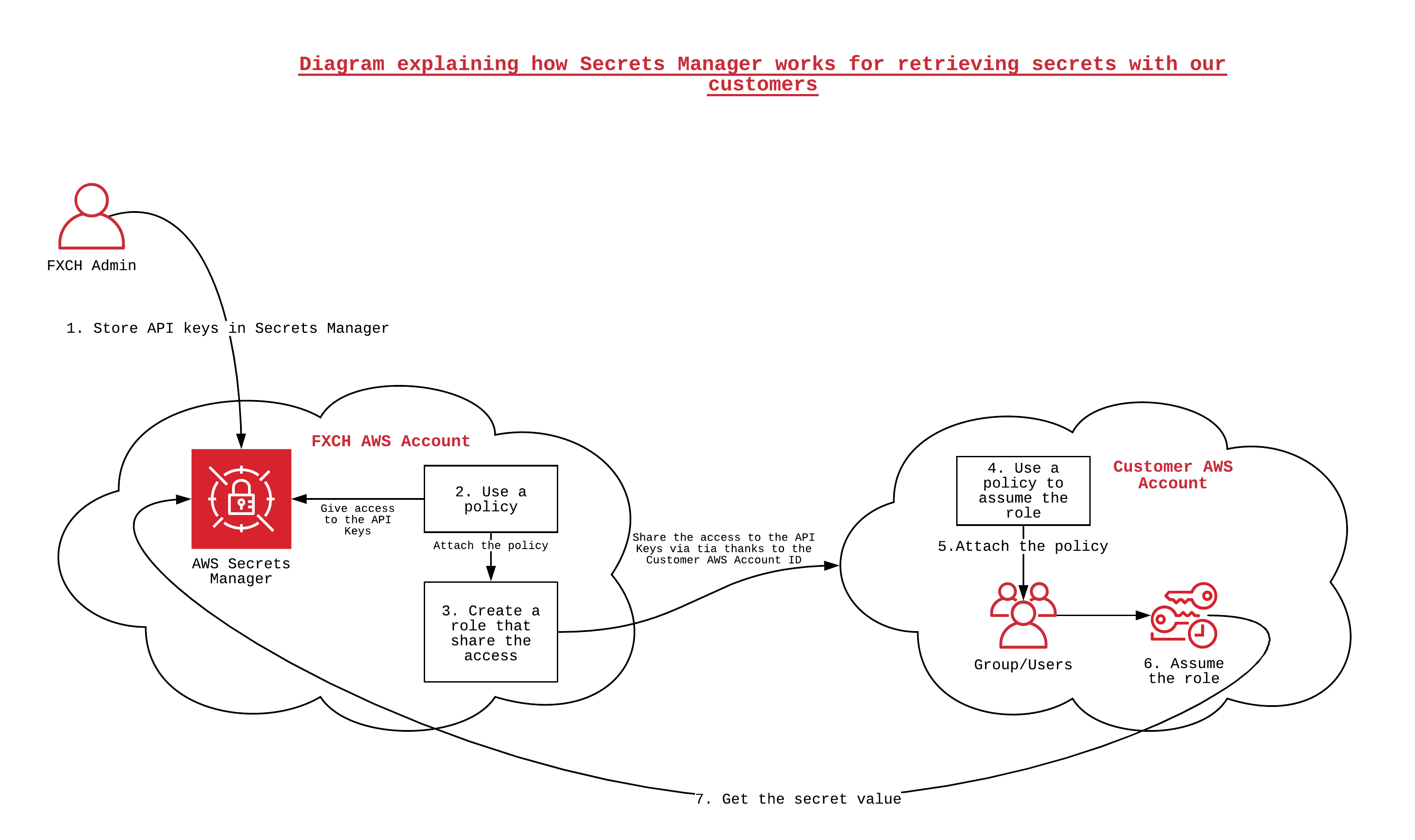
[[File: | [[File:SM1.png]] | ||
{{:AWS Secrets Manager, the best practices}} | {{:AWS Secrets Manager, the best practices}} | ||
Revision as of 18:56, 10 August 2021
AWS Secrets Manager, why do we use it?
There are much more possibilities with this AWS service. You can find more information about Secrets Manager below and also the most important part, the best practices.
What is it?
In the past, when you created a custom application to retrieve information from a database, you typically embedded the credentials, the secret, for accessing the database directly in the application. When the time came to rotate the credentials, you had to do more than just create new credentials. You had to invest time to update the application to use the new credentials. Then you distributed the updated application. If you had multiple applications with shared credentials and you missed updating one of them, the application failed. Because of this risk, many customers choose not to regularly rotate credentials, which effectively substitutes one risk for another.
Secrets Manager enables you to replace hardcoded credentials in your code, including passwords, with an API call to Secrets Manager to retrieve the secret programmatically. This helps ensure the secret can't be compromised by someone examining your code, because the secret no longer exists in the code. Also, you can configure Secrets Manager to automatically rotate the secret for you according to a specified schedule. This enables you to replace long-term secrets with short-term ones, significantly reducing the risk of compromise.
Important notions about Secrets Manager
Secret
In Secrets Manager, a secret consists of a set of credentials, user name and password, and the connection details used to access a secured service. You want to store these securely, and ensure only authorized users can access them. Secrets Manager always stores the secret text in an encrypted form and encrypts the secret in transit.
IAM Permission
Secrets Manager uses IAM permission policies to ensure only authorized users can access or modify the secret. You can attach these policies to users or roles, and specify which secrets the users can access.
ARN
An Amazon Resource Name (ARN) is a file naming convention used to identify a particular resource in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) public cloud. ARNs, which are specific to AWS, help an administrator track and use AWS items and policies across AWS products and API calls.
How does it work?
For implementing Secrets Manager easily in your Custom App, AWS provide AWS SDK which is a service that give tools like sample codes in many different programmatic languages. It also allows retrieving API Keys automatically when you need them. If you want more information about AWS SDK and how to implement Secrets Manager, go see the Developers wiki, here.
The services provided by Secret Manager
The best practices
Here are some best practices for managing and using API Keys that we strongly suggest following:
- Never store API Keys (especially the secret key) on your computer
- Use the keys from Secrets Manager, only when you need it.
- If you copy and paste the keys into your application, make sure that you delete everything in your clipboard.
- Retrieve API Keys from Secrets Manager programmatically and automatically via AWS SDK.